A Mouthful of Oral Lesions
Mouthful of Oral Lesions, Part 2
Photo Quiz
Self-Test Your Diagnostic Acumen

Case 1:
The mucocutaneous lesions seen in these photographs—facial cutaneous papules and oral papillomas—are among the most constant diagnostic features of what disease?
(Answer on next page.)
Photo Quiz—Answer
Case 1: Cowden disease These mucocutaneous lesions are the most constant diagnostic feature of Cowden disease (multiple hamartoma syndrome), a genodermatosis with an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. This disease is strongly associated with malignant tumors—especially those that involve the breast, thyroid, and GI and genitourinary tracts. In fact, the woman in these photographs had metastatic breast carcinoma and was undergoing palliative radiation therapy. The lesions in these photographs were discovered during the radiation therapy along with a goiter and axillary skin tags, which are also well-described features of Cowden disease.
These mucocutaneous lesions are the most constant diagnostic feature of Cowden disease (multiple hamartoma syndrome), a genodermatosis with an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. This disease is strongly associated with malignant tumors—especially those that involve the breast, thyroid, and GI and genitourinary tracts. In fact, the woman in these photographs had metastatic breast carcinoma and was undergoing palliative radiation therapy. The lesions in these photographs were discovered during the radiation therapy along with a goiter and axillary skin tags, which are also well-described features of Cowden disease.
Because the mucocutaneous manifestations of Cowden disease generally precede the development of neoplasia, early recognition of these lesions may permit early intervention that may prevent malignancy or facilitate prompt detection of commonly associated malignancies.
(Case and photographs courtesy of
Dr David L. Sherr.)
Continued on next page

Case 2:
(Answer on next page.)
Photo Quiz—Answer
 Case 2: Angioma
Case 2: Angioma
Biopsy proved this lesion to be a classic angioma. Such lesions are sometimes the result of localized trauma to the mucosa of the tongue. The differential diagnosis includes other nodules of the tongue, such as mucous cyst or carcinoma.
(Case and photograph courtesy
of Dr Joseph P. Bark.)
Continued on next page
Photo Quiz
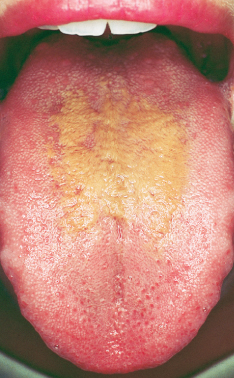
Case 3:
This discoloration on the tongue of a 26-year-old woman has been present for about a week. She is otherwise asymptomatic. Several weeks earlier, she had been treated for a urinary tract infection, but the medication had been discontinued before the discoloration occurred.
Is this a drug reaction?
(Answer on next page.)
Photo Quiz—Answer
 Case 3: Hairy tongue
Case 3: Hairy tongue
The diagnosis was hairy tongue, and the patient was assured that the condition was benign. She was instructed to brush the area regularly with a soft toothbrush. The discoloration cleared 3 weeks after it had appeared.
This condition is the result of hyperplasia of the filiform papillae. It can be a consequence of topical or systemic antibiotics, but in some persons, no cause can be established. Pigmentation within the area of hyperplasia is attributed to the activities of pigment-producing microorganisms.
(Case and photograph courtesy
of Dr Reynold C. Wong.)
Continued on next page
Photo Quiz
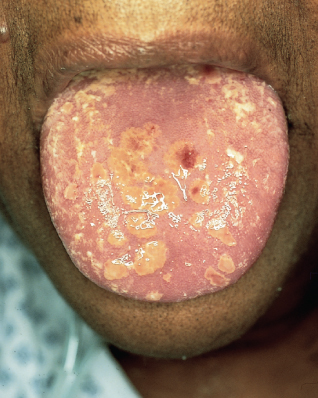
Case 4:
This 46-year-old African American woman has been taking corticosteroids for severe pulmonary sarcoidosis. Multiple erosions have developed on her hard palate along with tender, yellow-brown, firm papules on her tongue, some of which have eroded and bled.
What would you consider in the differential diagnosis?
(Answer on next page.)
Photo Quiz—Answer
 Case 4: Herpes simplex
Case 4: Herpes simplex
The differential diagnosis includes atypical herpes simplex, atypical oral sarcoidosis, and histoplasmosis. Results of a biopsy of one of the
lesions showed herpetic changes; culture showed herpes simplex virus (HSV).
In immunocompromised patients like this woman, HSV lesions are often atypical and appear ulcerative, necrotic, and erosive. Classically, HSV vesicles are grouped on an erythematous base.
(Case and photograph courtesy
of Dr Reynold C. Wong.)


